




Next: Complexity of SCG
Up: Scaled Conjugate Gradient
Previous: Main features of
As  and
and  are computed from their respective values at
step k-1, SCG has two parameters, namely the initial values
are computed from their respective values at
step k-1, SCG has two parameters, namely the initial values 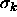 and
and
 . Their values are not critical but should respect the conditions
. Their values are not critical but should respect the conditions
 and
and  . Empirically Møller
has shown that bigger values of
. Empirically Møller
has shown that bigger values of  can lead to a slower convergence.
can lead to a slower convergence.
The third parameter is the usual quantity  (cf. standard
backpropagation).
(cf. standard
backpropagation).
In SNNS, it is usually the responsibility of the user to determine
when the learning process should stop. Unfortunately, the  adaptation mechanism sometimes assigns too large values to
adaptation mechanism sometimes assigns too large values to  when no more progress is possible. In order to avoid floating-point
exceptions, we have added a termination criterion
when no more progress is possible. In order to avoid floating-point
exceptions, we have added a termination criterion to SCG. The criterion is taken from the CGMs presented
in [P
to SCG. The criterion is taken from the CGMs presented
in [P 88]: stop when
88]: stop when

 is a small number used to rectify the special case of converging to a
function value of exactly zero. It is set to
is a small number used to rectify the special case of converging to a
function value of exactly zero. It is set to  .
.
 is a tolerance depending of the floating-point precision
is a tolerance depending of the floating-point precision
 of your machine, and it should be set to
of your machine, and it should be set to  , which is
usually equal to
, which is
usually equal to  (simple precision) or to
(simple precision) or to  (double
precision).
(double
precision).
To summarize, there are four non-critical parameters:
-
 . Should satisfy
. Should satisfy  . If 0, will
be set to
. If 0, will
be set to  ;
;
-
 . Should satisfy
. Should satisfy  . If 0,
will be set to
. If 0,
will be set to  ;
;
-
 . See standard backpropagation. Can be set to 0 if
you don't know what to do with it;
. See standard backpropagation. Can be set to 0 if
you don't know what to do with it;
-
 . Depends on the floating-point precision. Should be set to
. Depends on the floating-point precision. Should be set to
 (simple precision) or to
(simple precision) or to  (double precision). If
0, will be set to
(double precision). If
0, will be set to  .
.
Note: SCG is a batch learning method, so shuffling the
patterns has no effect.
Niels.Mache@informatik.uni-stuttgart.de
Tue Nov 28 10:30:44 MET 1995
 and
and  are computed from their respective values at
step k-1, SCG has two parameters, namely the initial values
are computed from their respective values at
step k-1, SCG has two parameters, namely the initial values 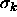 and
and
 . Their values are not critical but should respect the conditions
. Their values are not critical but should respect the conditions
 and
and  . Empirically Møller
has shown that bigger values of
. Empirically Møller
has shown that bigger values of  can lead to a slower convergence.
can lead to a slower convergence.
 (cf. standard
backpropagation).
(cf. standard
backpropagation).
 adaptation mechanism sometimes assigns too large values to
adaptation mechanism sometimes assigns too large values to  when no more progress is possible. In order to avoid floating-point
exceptions, we have added a termination criterion
when no more progress is possible. In order to avoid floating-point
exceptions, we have added a termination criterion 88
88
 is a small number used to rectify the special case of converging to a
function value of exactly zero. It is set to
is a small number used to rectify the special case of converging to a
function value of exactly zero. It is set to  .
.
 is a tolerance depending of the floating-point precision
is a tolerance depending of the floating-point precision
 of your machine, and it should be set to
of your machine, and it should be set to  , which is
usually equal to
, which is
usually equal to  (simple precision) or to
(simple precision) or to  (double
precision).
(double
precision).
 . Should satisfy
. Should satisfy  . If 0, will
be set to
. If 0, will
be set to  ;
;
 . Should satisfy
. Should satisfy  . If 0,
will be set to
. If 0,
will be set to  ;
;
 . See standard backpropagation. Can be set to 0 if
you don't know what to do with it;
. See standard backpropagation. Can be set to 0 if
you don't know what to do with it;
 . Depends on the floating-point precision. Should be set to
. Depends on the floating-point precision. Should be set to
 (simple precision) or to
(simple precision) or to  (double precision). If
0, will be set to
(double precision). If
0, will be set to  .
.