
One disadvantage of the above initialization procedure is the very simple selection of center vectors from the set of teaching patterns. It would be favorable if the center vectors would homogeneously cover the space of teaching patterns. RBF_Weights_Kohonen allows a self--organizing training of center vectors. Here, just as the name of the procedure already tells, the self--organizing maps of Kohonen are used (see [Was89]). The simplest version of Kohonen's maps has been implemented. It works as follows:
One precondition for the use of Kohonen maps is that the teaching patterns have to be normalized. This means, that they represent vectors with length 1. K patterns have to be selected from the set of n teaching patterns acting as starting values for the center vectors. Now the scalar product between one teaching pattern and each center vector is computed. If the vectors are normalized to length 1, the scalar product gives a measure for the distance between the two multiplied vectors. Now the center vector is determined whose distance to the current teaching pattern is minimal, i.e. whose scalar product is the largest one. This center vector is moved a little bit in the direction of the current teaching pattern:

This procedure is repeated for all teaching patterns several times. As a result, the center vectors adapt the statistical properties of the set of teaching patterns.
The resp. meanings of the three initialization parameters are:
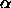 : It should be picked between 0 and
1. A learning rate of 0 leaves the center vectors unchanged. Using a
learning rate of 1 replaces the selected center vector by the current
teaching pattern.
: It should be picked between 0 and
1. A learning rate of 0 leaves the center vectors unchanged. Using a
learning rate of 1 replaces the selected center vector by the current
teaching pattern.
Note, that the described initialization procedure initializes only the center vectors (i.e. the link weights between input and hidden layer). The bias values of the neurons have to be set manually using the graphical user interface. To perform the final initialization of missing link weights, another initialization procedure has been implemented.